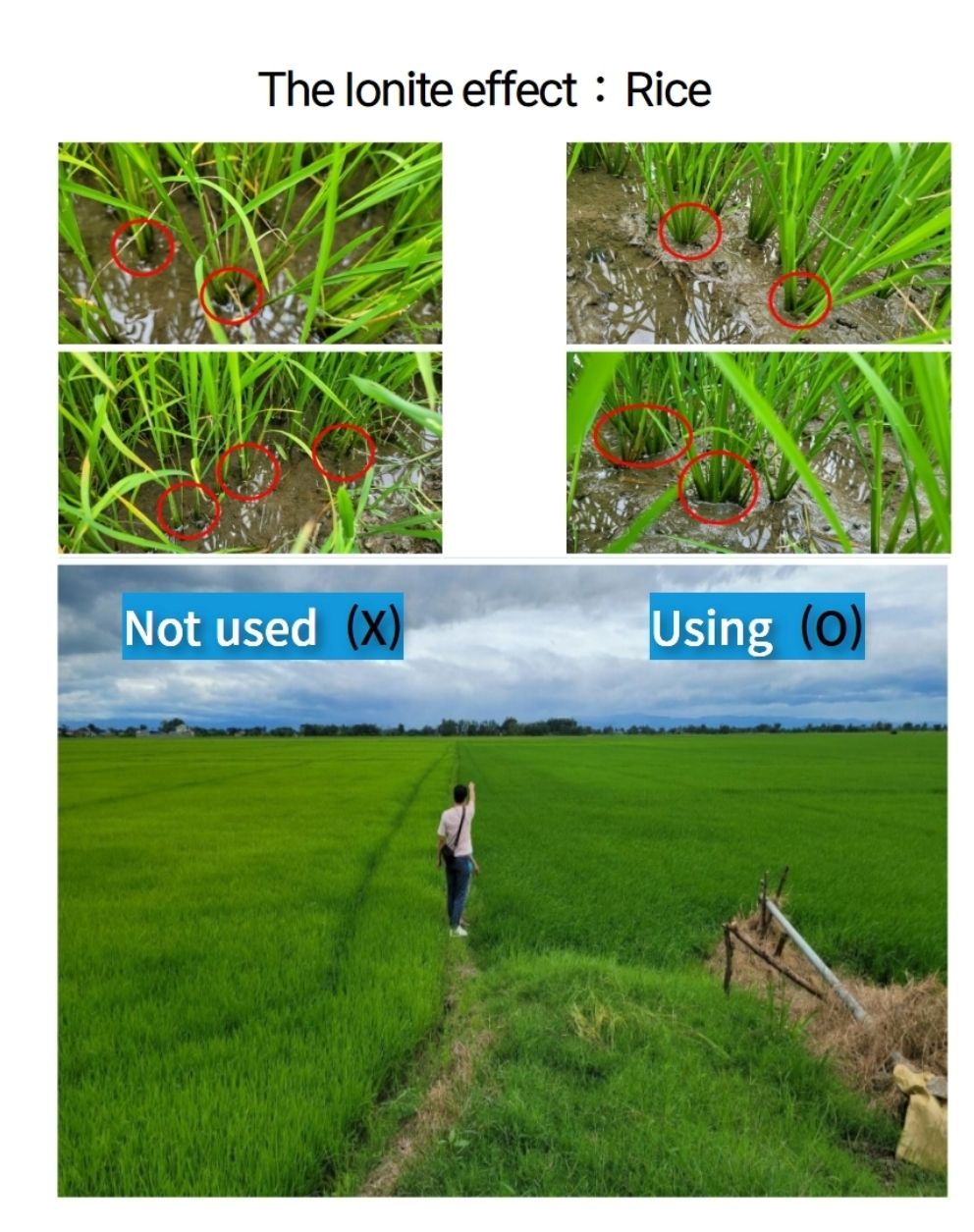









* Poultry
Ionite minerals offer various advantages for poultry breeding, disease prevention, and overall well-being. Here is a summary of the relevance of ionite minerals in poultry production:
1. Poultry Breeding:
Ionite minerals can help promote poultry breeding. Adequate supply of ionite minerals can enhance the reproductive capacity of poultry and increase productivity.
2. Survival Rate:
Ionite minerals can improve the survival rate of poultry. Proper levels of ionite mineral intake contribute to healthy growth and enhanced immune function, thus increasing poultry survival rates.
3. Disease Resistance:
Ionite minerals can strengthen poultrys anti-infection effects. Adequate supply of ionite minerals enhances the immune system of poultry, improving resistance to infections and reducing disease transmission.
4. Mortality Reduction:
Ionite minerals can decrease poultry mortality. Proper intake of ionite minerals helps maintain poultry health, boosts resistance to diseases, and reduces mortality rates. Additionally, ionite minerals can promote bone and muscle development due to the balanced mineral supply. Ionite minerals support normal metabolic activities and nutrient absorption, improving overall poultry health. Adequate intake of ionite minerals enhances resilience during stressful situations, strengthening poultry productivity and competitiveness.
5. Improved Stress Resilience:
Ionite minerals help enhance poultrys resilience to stressors. Stress can have negative effects on poultry growth and productivity. However, proper intake of ionite minerals improves resistance to stress and enhances poultrys ability to cope with challenging situations. This helps maintain productivity and strengthen competitiveness.
In summary, ionite minerals offer various benefits to poultry production, including improved health, increased survival rates, reduced infection and mortality rates, and enhanced stress resilience. These advantages contribute to the economic profitability and sustainable operations for poultry producers.
* Ruminants
1. Intake and Digestion:
Reptiles, which do not perform photosynthesis, need to consume minerals from the environment. They typically obtain minerals by eating plants or other animals. The ingested plant material undergoes digestion, where mineral components are transformed and digested through the action of enzymes.
2. Absorption and Translocation:
After the digestion process, the digested plant material is absorbed in the intestine or colon. Ionite minerals, including other minerals, can also be absorbed in the intestine or colon. Once absorbed, ionite minerals are transported throughout the body via the bloodstream.
3. Utilization and Metabolism:
Absorbed ionite minerals are transported into cells and utilized for various physiological functions. Ionite minerals interact with enzymes and regulate signaling pathways within the cells. These processes contribute to the maintenance of cell structure, enzyme activation, and participation in metabolic reactions, ensuring the functionality and stability of cells.
Metabolism encompasses various physiological processes, including energy production and substance conversion, within an organism. Ionite minerals, acting as essential components of enzymes, support and regulate metabolic processes along different pathways.
Ionite minerals play a crucial role as essential nutrients for the growth and development of reptiles. They are ingested and digested by reptiles, and once absorbed, they contribute to cellular functions such as maintaining cell structure, activating enzymes, and participating in metabolic reactions. These physiological functions of ionite minerals are vital for the growth and development of reptiles.